
Stephen
Terry, Director

From Arrogance to Destruction
Commentary
for the February 8, 2020 Sabbath School Lesson
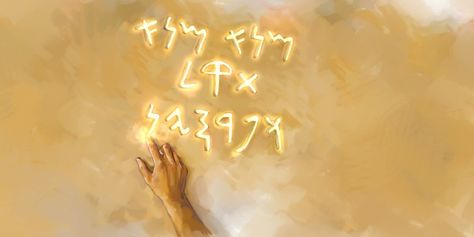 Suddenly the fingers of a
human hand appeared and wrote on the plaster of the wall, near the lampstand in
the royal palace. The king watched the hand as it wrote. His face turned pale
and he was so frightened that his legs became weak and his knees were knocking."
Daniel 5:5-6, NIV
Suddenly the fingers of a
human hand appeared and wrote on the plaster of the wall, near the lampstand in
the royal palace. The king watched the hand as it wrote. His face turned pale
and he was so frightened that his legs became weak and his knees were knocking."
Daniel 5:5-6, NIV
Approximately twenty-three years have passed since the
reign of Nebuchadnezzar had come an end in 562 BCE.[i] Babylon
has had a succession of brief rulers, Amel-Marduk, Neriglissar, and Labashi-Marduk,
followed by Nabonidus. While his involvement and the
circumstances of his elevation are not clear, Nabonidus
became king shortly after Labashi-Marduk, a child
king, was assassinated. He departed for military campaigns in Anatolia, leaving
his son, Belshazzar, in charge. Perhaps because he had confidence in his son's
judgment, he delayed his return for ten years from 553-543 BCE, staying at Tayma Oasis in Arabia. He also may not have felt
comfortable in Babylon as he worshipped and elevated the moon god, Sin in the
Babylonian pantheon, while the priests of the city maintained that Marduk was the supreme deity. Whatever the reason, any
concerns were set aside upon learning of invasion from the North. He gathered
his forces and engaged with Cyrus the Great, who was leading a Persian force
against the Babylonians. He met Cyrus's army at Opis
on the eastern side of the Tigris River. Suffering defeat in that encounter, Nabonidus withdrew toward the Euphrates, perhaps expecting
the Persians to follow. However, Cyrus had a better idea. Instead, his forces
followed the Tigris to the gates of Babylon and laid siege to the city. We know
of no efforts on the part of Nabonidus to lift that
siege. Perhaps he, like Belshazzar, felt that the walls could not be breached.
We are told that, far from being fearful of the army
outside his gates, Belshazzar threw a party in the palace where wine flowed
freely and judgment was impaired. He may have pointed out to his nobles that
the gods of Babylon had preserved them thus far and would continue to do so. He
and his nobles praised and toasted those gods. Then he may have thought to
reinforce the perception of the power of the Babylonian gods by recalling a
victory from the past, the destruction of Jerusalem by Nebuchadnezzar in 586
BCE. Calling for the vessels looted from the Jerusalem Temple. When they were
brought out, he encouraged everyone to drink from those vessels in praise of
the more powerful Babylonian deities. At this provocation, we are told that God
could no longer remain silent.
A disembodied hand suddenly appears and begins writing
on the wall. The message being written was to be seen by everyone, being
written close to one of the lampstands in the hall and therefore not hidden in
the shadows. The writing was in Aramaic, which had become the common tongue of
the Jews, evolving from Hebrew. We are told that Belshazzar shook with fear,
perhaps in part at the sight of the disembodied hand, and perhaps also because
he was unable to read the message it gave. At the presence of such an
apparition, the hall may have become deathly quiet as the revelers ceased their carousing to watch. Then the silence would have ended as they attempted to discern the meaning. However, no one present could do so. Belshazzar then sent for Babylonian scholars to accomplish the task. The Bible refers to them as "enchanters, astrologers, and diviners." These were similar to the "wise men" that would later travel to Israel after determining that the birth of the Messiah had taken place. Because of their education, they may have been able to read the Aramaic writing, but were at a loss to interpret it, even though Belshazzar had promised to make the one who could, third ruler in the kingdom after himself and Nabonidus. Their failure only increased the
king's fear.
The queen, perhaps the wife of Nabonidus,
hearing the commotion came into the hall and reminded Belshazzar of Daniel, who
had interpreted dreams for Nebuchadnezzar and that he was still available to
assist. Belshazzar ordered him brought to the hall. Ironically, Daniel's
Babylonian name, Belteshazzar, meant the same as
Belshazzar's, "Bel protect the king." Yet
Daniel was about to reveal the loss and fall of the kingdom of Babylon. Not
knowing what to expect, the prince reminded Daniel of the reward of being made
third ruler in the kingdom. Daniel, who perhaps knew there would soon be no
kingdom to rule, demurred. Looking around and seeing the articles from the
Temple in the hands of Belshazzar and his drunken court, he was not pleased.
With the spirit of so many prophets before him, he stood before the profligate
king and reminded him of the events recorded in Daniel, chapter 4, pointing out
that he knew what had happened and ignored it. Perhaps his father's elevation
of the moon god over the existing gods of Babylon caused him to feel he had
liberty to demote all gods under Sin. Whatever Belshazzar's reasons, Daniel was
having none of it.
He explained this was the reason the hand had appeared.
Then he translated the writing and gave the interpretation. The word "Mene," repeated twice for emphasis, and meaning
"numbered," meant essentially the same as in modern English when we
say "Your number is up." His reign had come to an end. The word,
"Tekel," revealed that Belshazzar did not
have the weight required for his position. He had replaced the humility of
Nebuchadnezzar with arrogance in ruling the empire. That arrogance had now
extended even to his treatment of the God Nebuchadnezzar honored. Therefore his
reign was to end. The final word Daniel interpreted, "Parsin,"
had a double meaning. It meant that the kingdom would be divided, perhaps more
accurately torn from him by a power greater than his own, and in a word play on
those besieging the city. The word also means Persia. The dividing then could
be seen as being ordered by God but accomplished by the Persian
"dividers." In spite of the adverse interpretation, Belshazzar made
good on his promise to make Daniel third ruler in the kingdom. But the Bible
tells us that he did not outlive Daniel but lost his life that same night.
How the fall of Babylon occurred is not entirely clear.
An account by Herodotus states that a spy entered the city and was then able to
open the gates for the Persians. Another account in the Nabonidus
Chronicle, perhaps written during the reign of Darius I, says that the citizens
themselves opened the gates, tired of Belshazzar's rule and his insults to Marduk. According to Herodotus,[ii] who never visited Babylon and was
writing about it a century later, the Persians diverted the Euphrates and
accessed the city through the river gates. This is the account that apparently
Uriah Smith refers to in his book, "Daniel and the Revelation."[iii] Nonetheless,
the Bible says nothing about the Persians diverting the river and making an
aggressive attack to conquer the city. Instead, Isaiah says that God will open
the gates for Cyrus,[iv] but does not elaborate as to how. A more
contemporary account seems to agree with those that say the citizens welcomed
him and opened the gates. The "Cyrus Cylinder," an ancient cuneiform
tablet (539-530 BC) that records the conquest of Babylon states that the city
was taken "without fighting or battle." While legend says Belshazzar
died in battle commanding forces against the Persians, the actual ruler, Nabonidus, capitulated and was treated well by the
Persians, although exiled. The golden head of Daniel, chapter 2, had reached
its end with the defeat of Babylon and now began the time of the chest and arms
of silver as the Persian Empire rose to power.
[i] The
dates in this narrative are taken from, "Chronological Charts of the Old
Testament," John H Walton, The Zondervan
Corporation, 1978
[ii] "Histories,"
Herodotus, 1.189-191
[iii] "Daniel
and the Revelation," Uriah Smith, Southern Publishing Association,
Nashville, TN, 1944
